Introduction
Lately I was trying to port kali nethunter to my old phone with supported external wifi card and things to be worked without much issues that I have found while using custom pre-built kali nethunter roms and custom kernel and it appears non of them worked in a stable way and not much support for the external wifi cards (Like the well-known TP-LINK W722N v2) and some other tools. So I have decided to create my own custom build for kali nethunter and this blog post will be about my walkthrough on how I have created my custom build for my unsupported phone.
Requirements
First it’s recommended that you have PC or Laptop with ubuntu based linux distro installed on it, In this walkthrough I have used Linux Mint with adb and fastboot tools installed.
Also you might need a windows virtual machine to use Mi Unlock tool for this task only.
Phone used in this walkthrough is Poco X3 NFC.
- Manufacturer: Xiaomi
- Full Name: Xiaomi Poco X3 NFC
- Codename: Surya
- Operating System: Upgradable to Android 13
- Processor: Qualcomm Snapdragon 732G
- Architecture: Arm64
- Wi-Fi: 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac, Dual-band, Wi-Fi Direct, Wi-Fi Display, DLNA, Hotspot Can be used for Monitor/Injection Mode!
Then you need an android phone with bootloader unlocked. In case of Xiaomi you will need the following steps:
- Sign in to your Mi Account
- Activate the Developer options (Settings -> About Phone -> ‘Tab 3 times on MIUI version’)
- Go to Additional Settings -> Developer Options -> Enable OEM Unlocking and Mi Unlock status (Permission required: tap Agree) -> Add Account and device
- The toast message should appear “Added successfully. Mi Account is associated with this device now.”
- Now Shut down your phone manually, and hold Volume down key and Power button to enter Fastboot mode.
- Download the Mi Unlock tool from MIUI official website on you windows VM and connect your phone to PC using USB cable and pass it to the windows VM you have.
-
Sign in to your Mi Account in Mi Unlock with the same account on your phone for sure, After that it will check if phone connected and click “Unlock”.
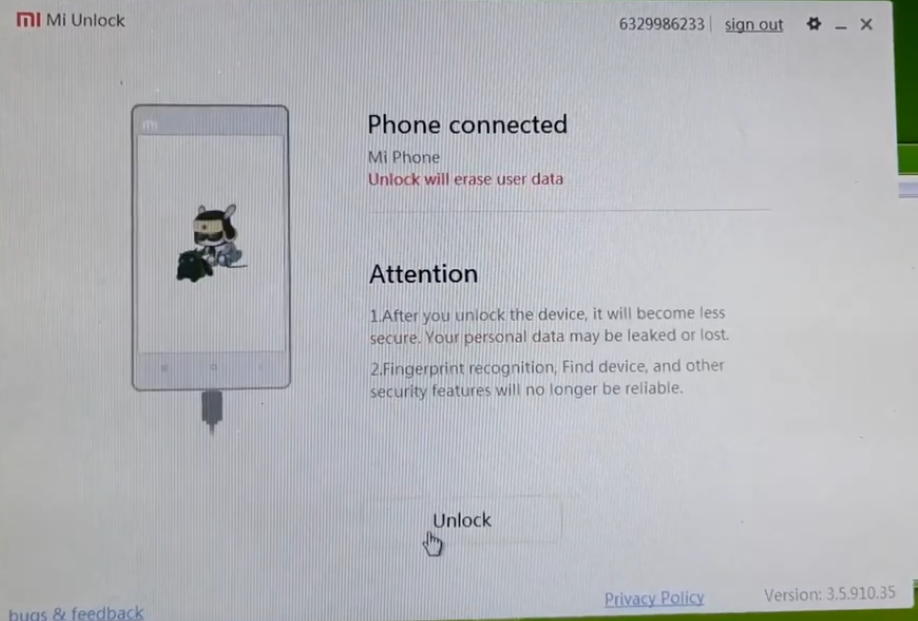
-
Unfortunately you will have to wait like 168 hours to unlock so after this period of time you will be able to unlock you phone correctly.
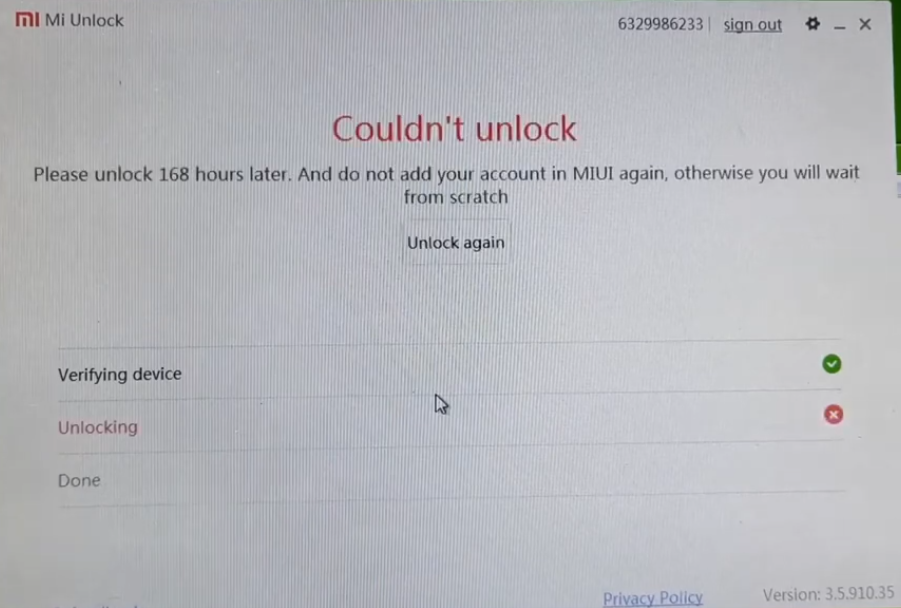
- So after this period repeat these process again and unlock it with Mi Unlock and the phone should be unlocked successfully.
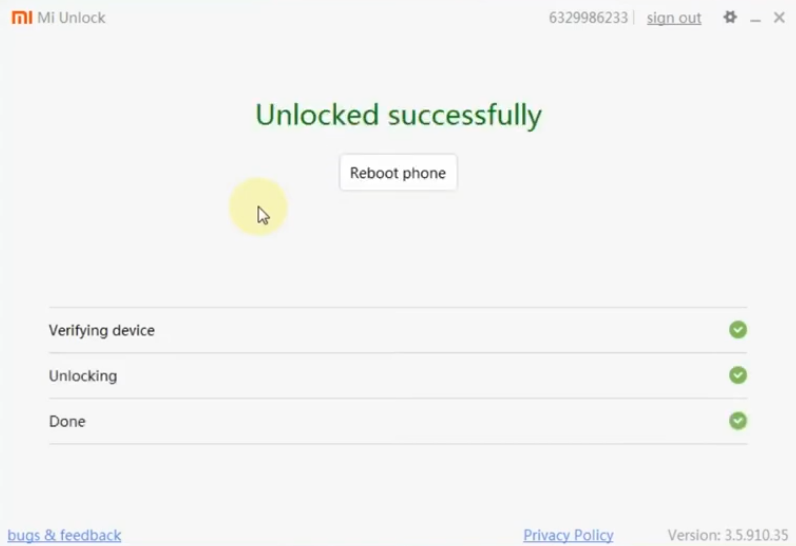
Be informed that this process will erase all your phone data so it’s recommended to backup your data before starting. Also unlocking your phone it makes you phone vulnerable so make sure you are using an old phone that you are not using with any personal sensitive data.
Flash Custom ROM with Custom Recovery
Now we will have to flash custom ROM to be used with kali nethunter using custom recovery called TWRP and check if TWRP have an official build for your device here: https://twrp.me/Devices/ but I didn’t find my phone right there so I have searched for unofficial build of TWRP following with my phone codename.
Then I have used Lineage Custom ROM and I have found an official build already for my Surya phone. 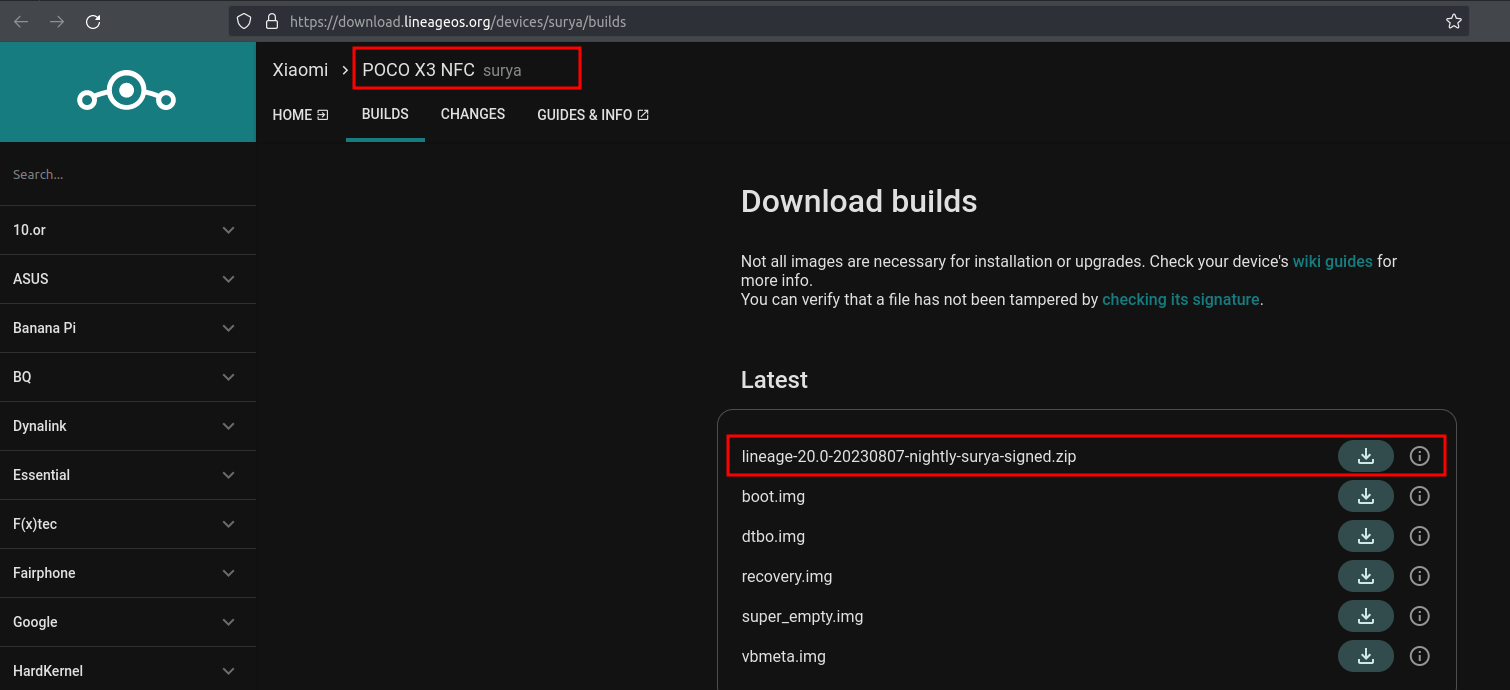
Also it’s recommended to download Magisk Manager to manage applications that requires root permissions and flashing modules. We will using it later to flash our custom build of kali nethunter.
So now we have 3 Files requried:
- TWRP Custom Recovery
- LineageOS Custom ROM
- Magisk Manager APK File
Now go to “Developer Options”, enable “USB debugging” and then connect your phone to the laptop via USB cable and run adb devices, You should see the following output. 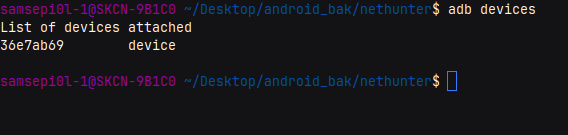
So everything is prepared now, Start the flashing process.
- Reboot to the Fastboot Mode
adb reboot-bootloader - Flash and boot from TWRP custom recovery
fastboot boot twrp-3.5.2_10-10-surya.img # write twrp image name -
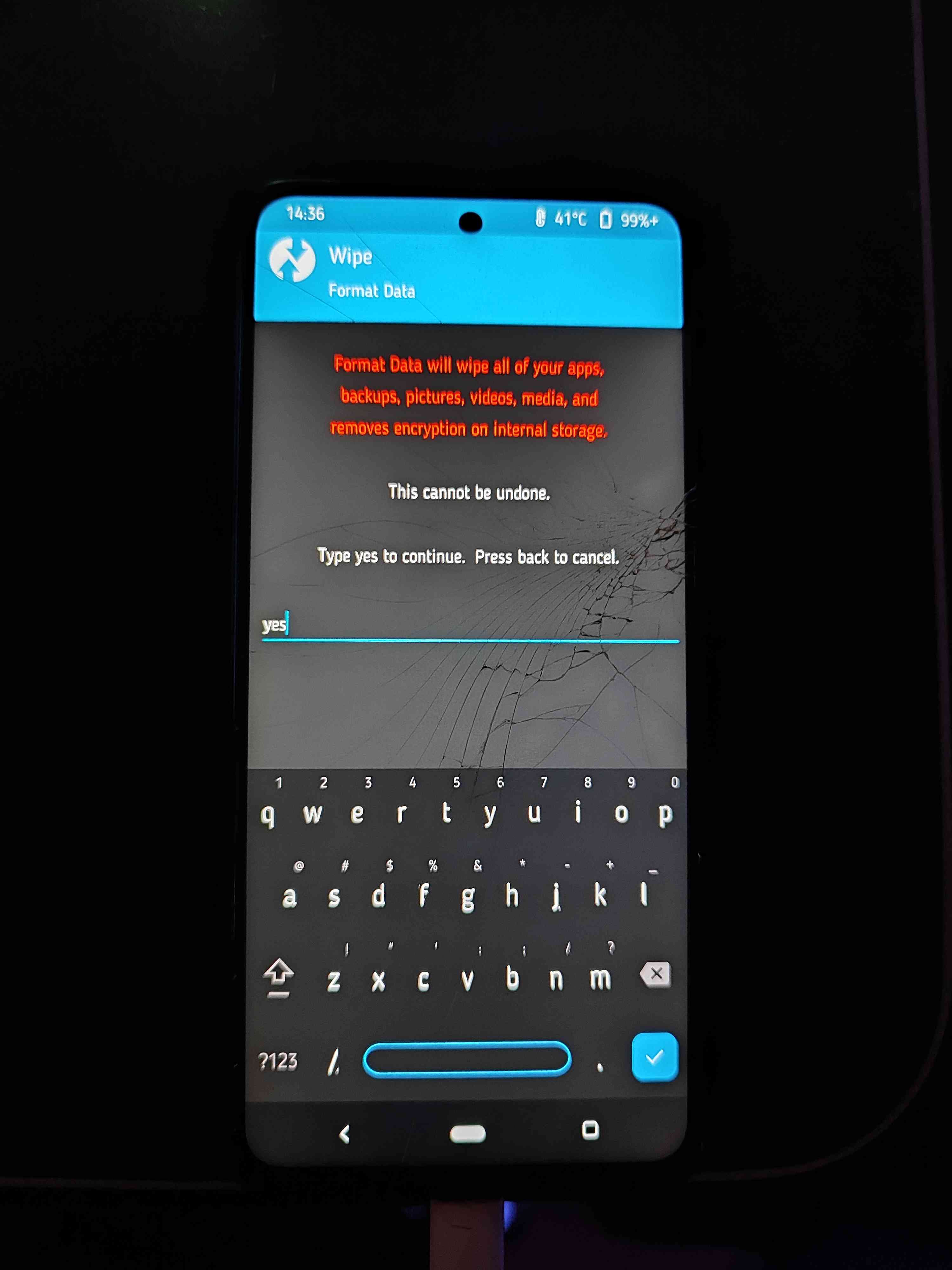
You should see TWRP custom recovery opened, Now go to (Wipe -> Format Data) and type “yes” then hit enter.
-
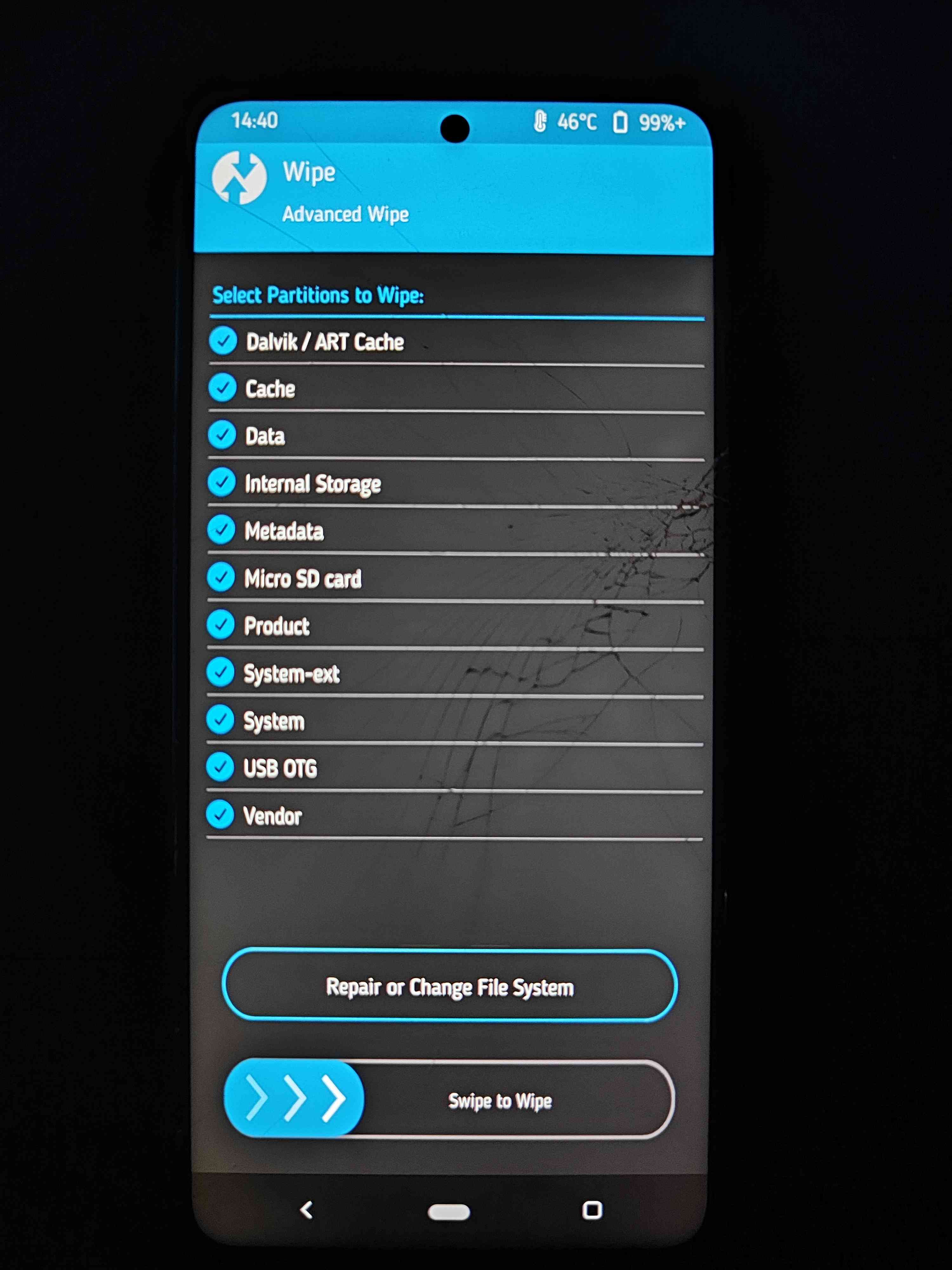
Also again go to (Wipe -> Advanced Wipe) And select everything to be wiped.
- Now back to your labtop, Push LineageOS custom ROM to the phone.
adb push lineage-20.0-20230731-nightly-surya-signed.zip /bluetooth - Change Magisk Manager APK file extension to be
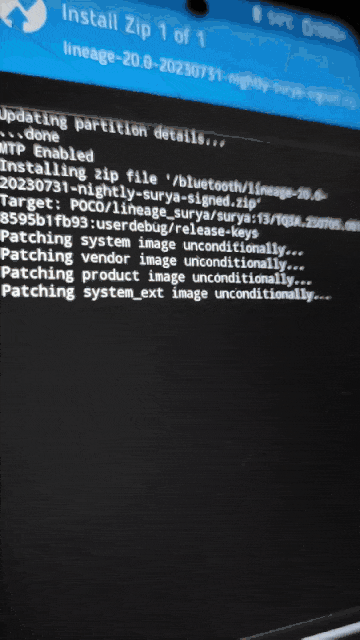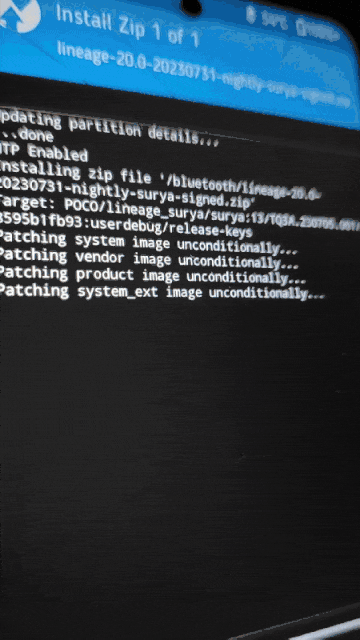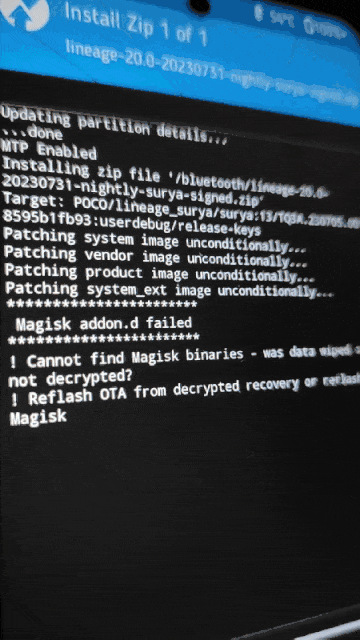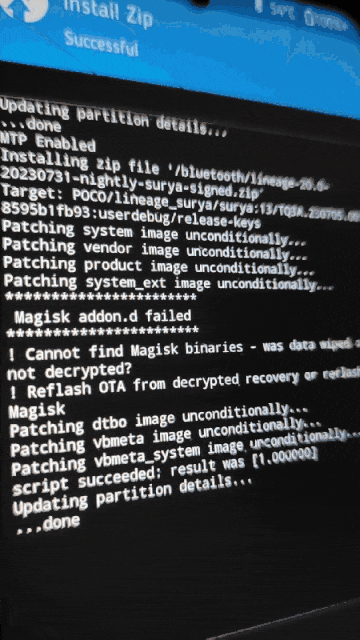
.zipinstead of.apkand push it to the phone.cp Magisk-v26.1.apk Magisk-v26.1.zip adb push Magisk-v26.1.zip /bluetooth - Back to phone, Go to (Install -> “Up A Level” -> bluetooth -> “Select the custom ROM file” -> Swipe to confirm flash)
- Then flash Magisk like we did with custom ROM
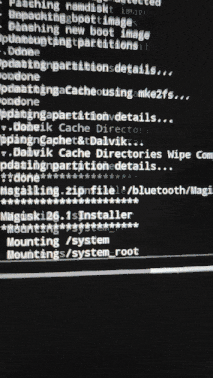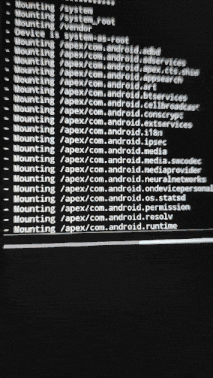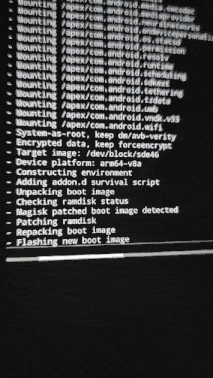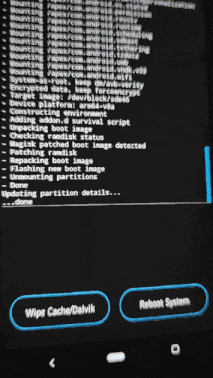
- Now reboot the device

- After device rebooted successfully, Enable the “USB Debugging” again from “Developer Options” and push magisk manager apk file to the phone
adb push Magisk-v26.1.apk /storage/emulated/0 - Then open the file manager, Click and install the magisk application. It may ask for reboot so go ahead.
I didn’t want to install GApps as I was afraid to make any conflicts or causing any unstable behavior, But you can try it yourself after finishing the whole process.
Find Kernel Sources and Making a Test Kernel
Before going any further I highly recommend to read the official Kali Nethunter Documentation as it’s very useful and I will quote alot from it.
So now we need a supported kernel source to work with, LineageOS have their opensource kernels available on github. In my case I will clone the kernel version “4.14” of Surya phone from https://github.com/LineageOS/android_kernel_xiaomi_surya branch Lineage-20 so it will be compatible with our LineageOS custom ROM.
After cloning the kernel source open it and clone https://gitlab.com/kalilinux/nethunter/build-scripts/kali-nethunter-kernel inside the root of the kernel’s directory.
git clone https://github.com/LineageOS/android_kernel_xiaomi_surya.git
cd android_kernel_xiaomi_surya
git clone https://gitlab.com/kalilinux/nethunter/build-scripts/kali-nethunter-kernel.git
Find your best matching local.config example file, for me I will use local.config.allinone config and will modify it.
cp local.config.examples/local.config.example.allinone local.config
To avoid issues while building the kernel, We will modify the local.config to use newer toolchains, So instead of using linaro-4.9 we will use linaro-5.5 like following.
CROSS_COMPILE_ARM32_SRC="https://kali.download/nethunter-images/toolchains/linaro-armhf-5.5.tar.xz"
CCD32="${TD}/linaro-armhf-5.5"
CROSS_COMPILE_SRC="https://kali.download/nethunter-images/toolchains/linaro-aarch64-5.5.tar.xz"
CCD="${TD}/aarch64-5.5"
It’s better to install these packages instead installing it from build.sh script as it will be more faster to do it in oneline than looping in each package.
apt install axel bc binutils-aarch64-linux-gnu build-essential ccache curl device-tree-compiler pandoc libncurses5-dev lynx lz4 fakeroot xz-utils whiptail zip unzip
Also before running ./build.sh there’s syntax error in line 847 so replace THREADS = 10 with THREADS=10 and then run the script.
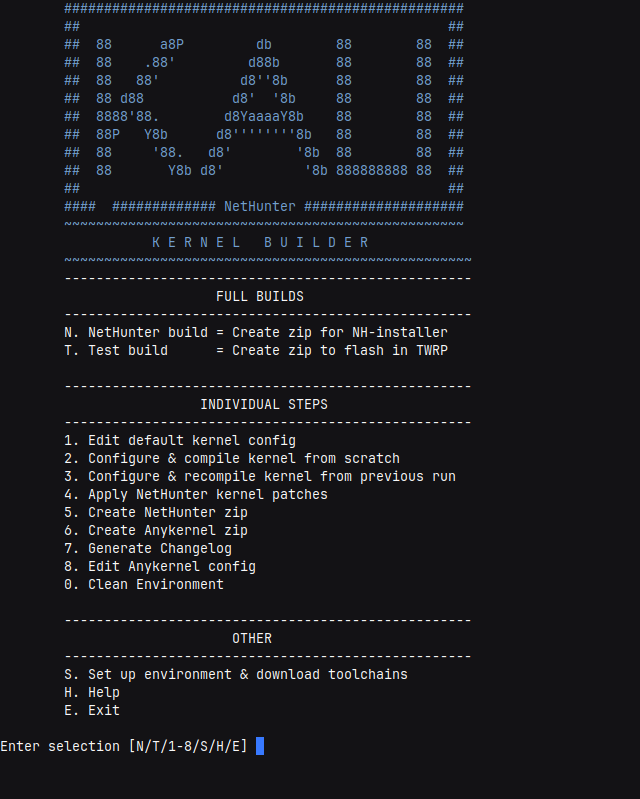
- Select “S. Setup Environment and download toolchains.”
- Then build test kernel so select “2. Configure & compile kernel from scratch”
- Select your device’s defconfig, In my case I have selected “surya_defconfig”
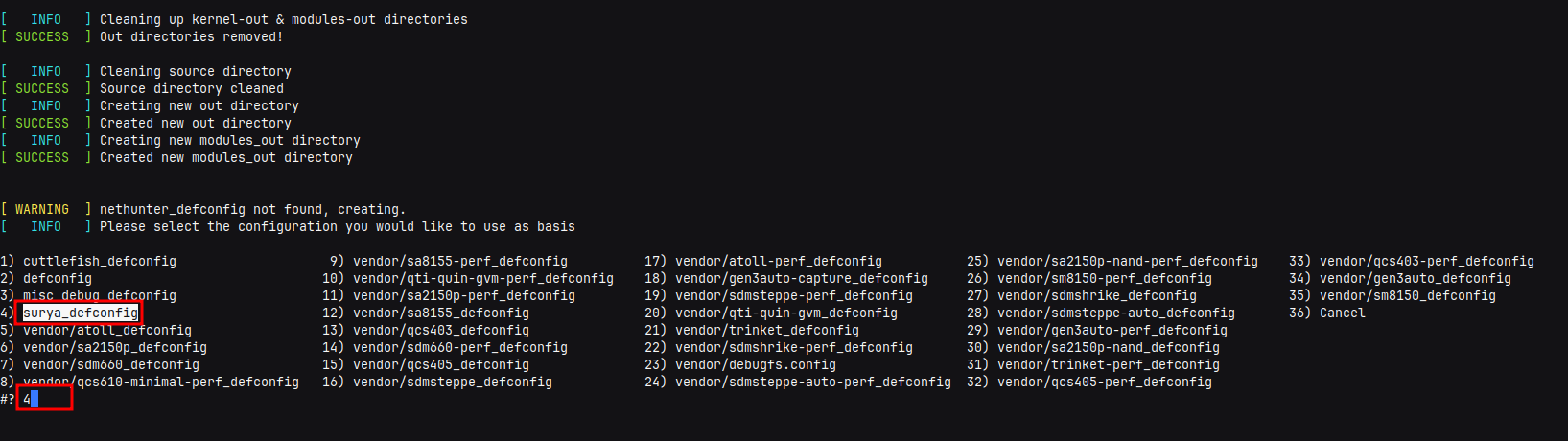
- Type
yand press tab and click “Save” to save the current configuration to.configfile then “Exit”, It’s just a test kernel it will be modified later then wait for it to finish kernel compiling. - If build was successful, select “8. Edit Anykernel config” to add some device details like codename, boot_block, slot_device, etc.
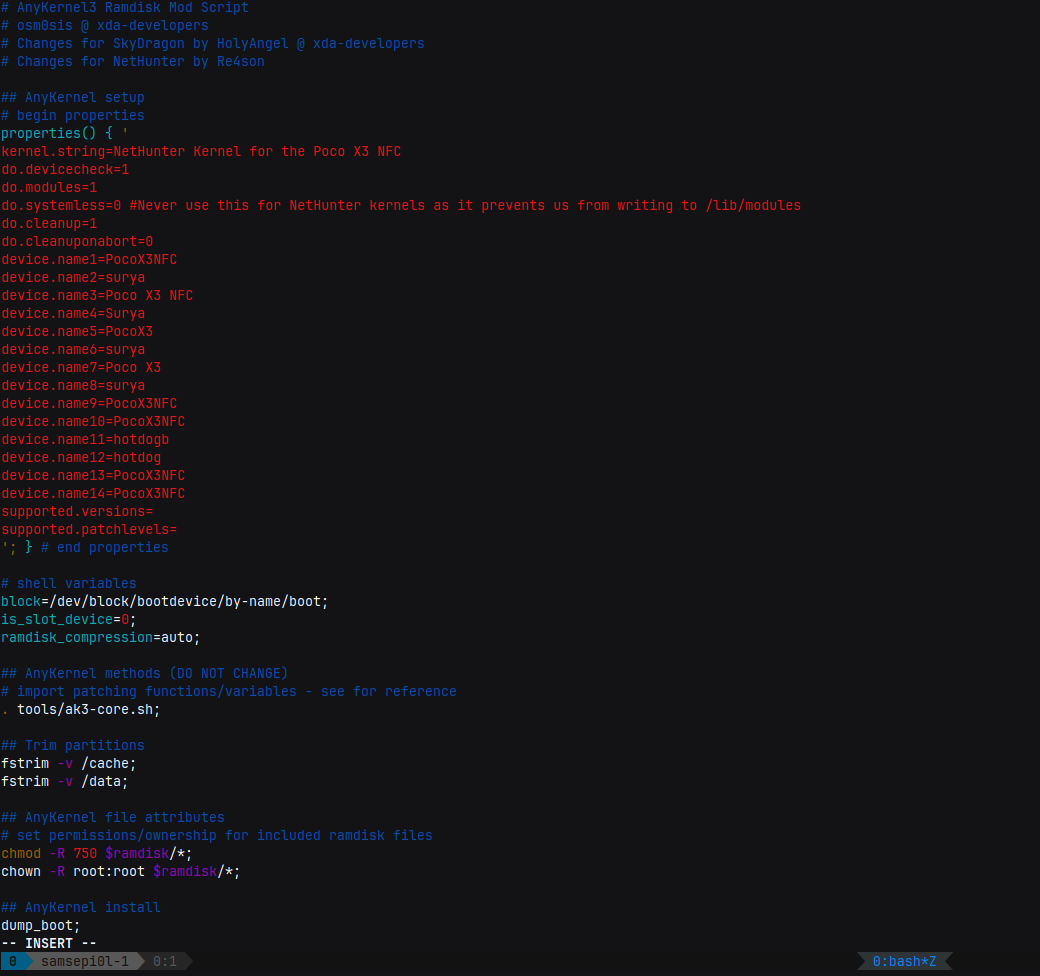
- Now let’s create our first test kernel, Select “6. Create Anykernel zip”
- It will be available at
kali-nethunter-kernel/output/anykernel-NetHunter.zip - Flash the kernel like we flashed the custom ROM before in TWRP custom recovery.
adb reboot-bootloader fastboot boot twrp-3.5.2_10-10-surya.img adb push anykernel-NetHunter.zip /bluetooth # Go to install -> Up A Level -> bluetooth -> anykernel-NetHunter.zip and swipe to flash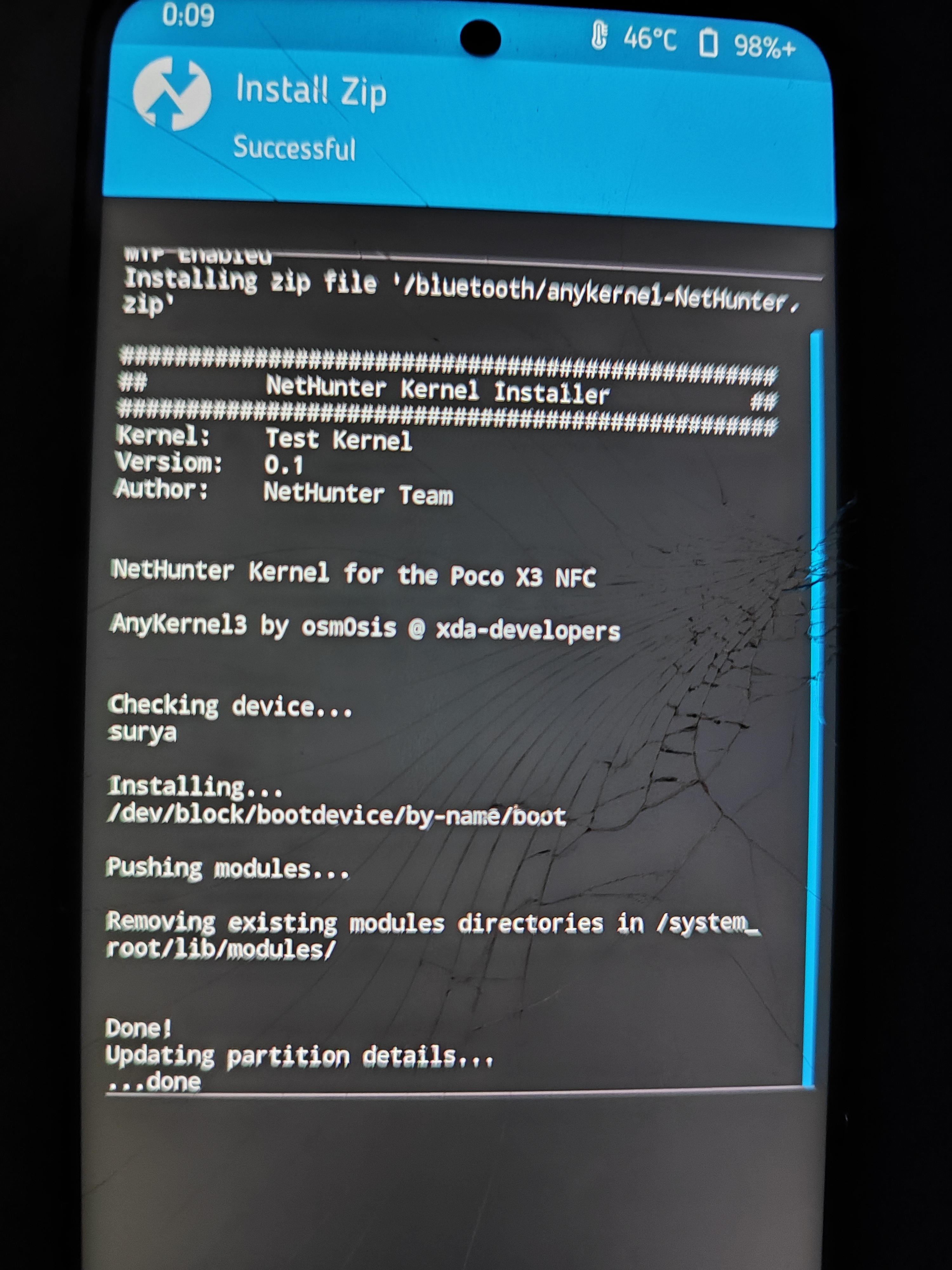
Patching the Kernel
As the Kali Nethunter documentation mentioned that some devices need additional patches to avoid build errors, Which it can be applied from their build.sh script.
So run ./build.sh and select “4. Apply NetHunter kernel patches” and then select the patch directory closest matching to your kernel version, In my case the kernel version is 4.14, After that apply every patch in the list but if it showed message like Warning: The test run completed with errors, apply the patch anyway? don’t apply it and skip it to another patch and so on.
If you have created a fork from the kernel source, You should commit each patch you made in the kernel source.
Configuring the Kernel
Now in the kernel configuration section select “3. Configure & recompile kernel from previous run” and type y to enter the kernel configuration menuconfig page and do the following steps.
The next steps are taken from Kali Nethunter Official Documentation, Please refer to it if you face any kind of issues.
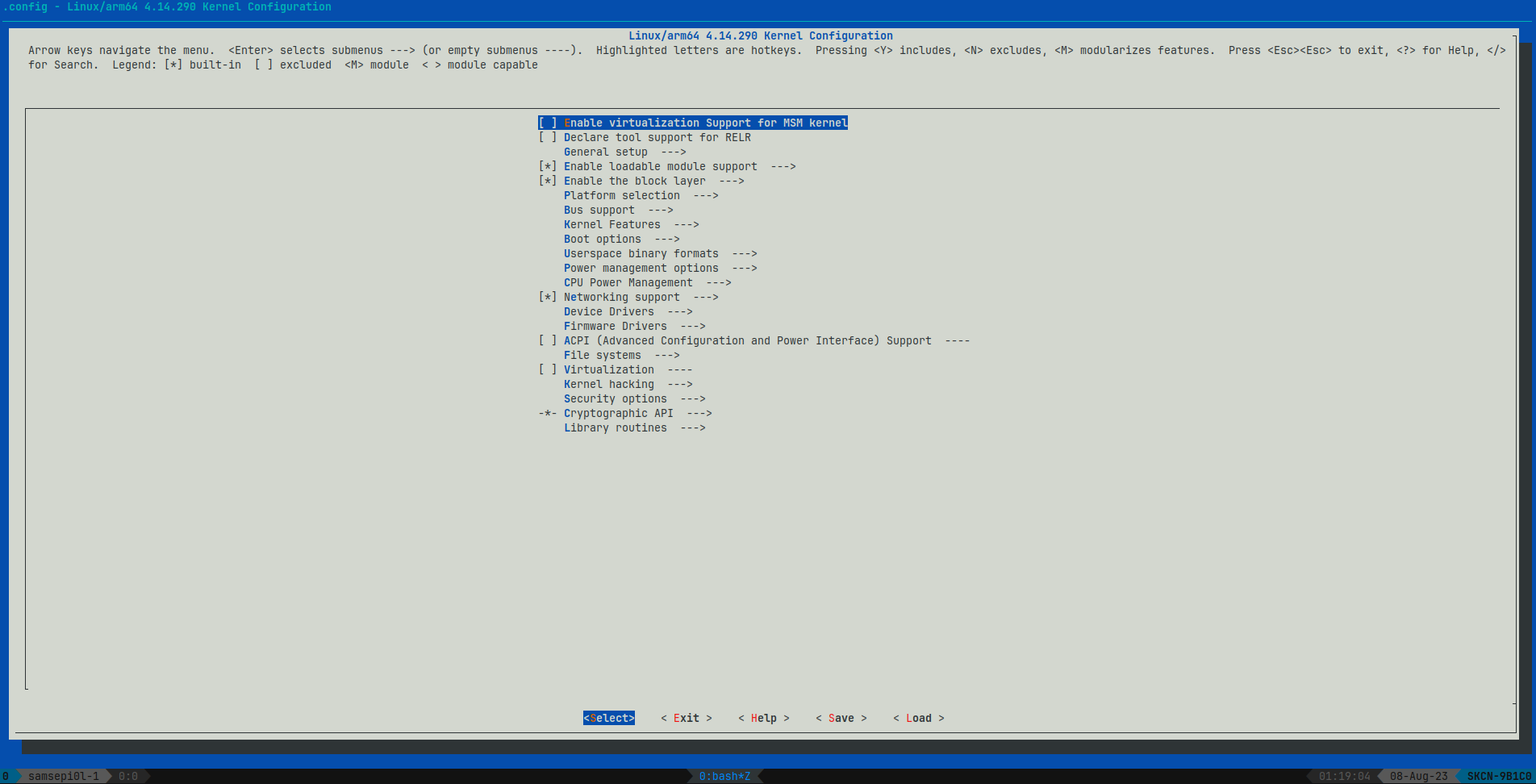
- In section General Setup
- Select Local version - append to kernel release and clear the Local version
- Set Default hostname to kali
- Check [*] System V IPC (CONFIG_SYSVIPC=y)
- In section [*] Enable loadable module support
- Check [*] Module unloading
- Check [*] Forced module unloading
- Check [*] Module versioning support
- In section [*] Boot options
- Check [*] Build a concatenated Image.gz/dtb by default
- Select Appended DTB Kernel Image name (Image.gz-dtb) and make sure that Image.gz-dtb is selected.
- In section [*] Networking support ->Bluetooth subsystem support -> Bluetooth device drivers
- Check <*> HCI USB driver
- Check [*] Broadcom protocol support
- Check [*] Realtek protocol support
- Check <*> HCI UART driver
- Check [*] UART (H4) protocol support
- Check <*> HCI BCM203x USB driver
- Check <*> HCI BPA10x USB driver
- Check <*> HCI BlueFRITZ! USB driver
- Check <*> HCI VHCI (Virtual HCI device) driver
- In section Device Drivers -> Android
- Check [*] Android Binder IPC Driver
- In section [*] Networking support -> Wireless
- Check [*] cfg80211 wireless extensions compatibility
- Check <*> Generic IEEE 802.11 Networking Stack (mac80211)
- Check [*] Enable mac80211 mesh networking (pre-802.11s) support
- In section Device Drivers -> [*] Network device support -> <*> USB Network Adapters
- Check <*> USB RTL8150 based ethernet device support
- Check <*> Realtek RTL8152/RTL8153 Based USB Ethernet Adapters
- In section Device Drivers -> [*] Network device support -> [*] Wireless LAN
- Check [*] Atheros/Qualcomm devices
- Check <*> Atheros HTC based wireless cards support
- Check <*> Linux Community AR9170 802.11n USB support
- Check <*> Atheros mobile chipsets support
- Check <*> Atheros ath6kl USB support
- Check [*] MediaTek devices
- Check <*> MediaTek MT7601U (USB) support
- Check [*] Ralink devices
- Check <*> Ralink driver support —> OPEN
- Check <*> Ralink rt2500 (USB) support
- Check <*> Ralink rt2501/rt73 (USB) support
- Check <*> Ralink rt27xx/rt28xx/rt30xx (USB) support
- Check [*] rt2800usb - Include support for rt33xx devices
- Check [*] rt2800usb - Include support for rt35xx devices (EXPERIMENTAL)
- Check [*] rt2800usb - Include support for rt3573 devices (EXPERIMENTAL)
- Check [*] rt2800usb - Include support for rt53xx devices (EXPERIMENTAL)
- Check [*] rt2800usb - Include support for rt55xx devices (EXPERIMENTAL)
- Check [*] rt2800usb - Include support for unknown (USB) devices
- Check [*] Realtek devices
- Check <*> Realtek 8187 and 8187B USB support
- Check <*> Realtek rtlwifi family of devices
- Check <*> RTL8723AU/RTL8188[EU/CR]U/RTL819[12]CU (mac80211) support
- Check [*] Include support for untested Realtek 8xxx USB devices (EXPERIMENTAL)
- Check [*] ZyDAS devices
- Check <*> USB ZD1201 based Wireless device support
- Check <*> ZyDAS ZD1211/ZD1211B USB-wireless support
- Check <*> Wireless RNDIS USB support
- In section Device Drivers -> Multimedia support
- Check [*] Digital TV support
- Check [*] Software defined radio support
- Remove [ ] Autoselect ancillary drivers (tuners, sensors, i2c, spi, frontends)
- In section Device Drivers -> Multimedia support -> Media USB Adapters
- Check <*> AirSpy
- Check <*> HackRF
- Check <*> Mirics MSi2500
- In section Device Drivers -> Multimedia support ->Customize TV tuners Remove and Uncheck all
- In section Device Drivers -> Multimedia support -> Customize DVB Frontends
- Check [*] Realtek RTL2830 DVB-T
- Check [*] Realtek RTL2832 DVB-T
- Check [*] Realtek RTL2832 SDR
- Check [*] Silicon Labs Si2168
- Check [*] ZyDAS ZD1301
- In section Device Drivers -> USB support
- Check <M> USB Modem (CDC ACM) support (For 3.x Kernel)
- Check <*> USB Modem (CDC ACM) support (For 4.x Kernel and above)
- Check <*> USB Gadget Support —> OPEN (For 4.x Kernel and above)
- Check [*] Generic serial bulk in/out
- Check [*] Abstract Control Model (CDC ACM)
- Check [*] Object Exchange Model (CDC OBEX)
- Check [*] Network Control Model (CDC NCM)
- Check [*] Ethernet Control Model (CDC ECM)
- Check [*] Ethernet Control Model (CDC ECM) subset
- Check [*] RNDIS
- Check [*] Ethernet Emulation Model (EEM)
- Check [*] Mass storage
Finaly the kernel configuration has been done, Save and Exit the menuconfig to start the kernel compiling.
I have done some modifications to fix some errors while compiling the kernel, Check kernel source code fork with all my modifications and patches https://github.com/r0ttenbeef/android_kernel_xiaomi_surya
Build Kali Nethunter Full
According to https://gitlab.com/kalilinux/nethunter/build-scripts/kali-nethunter-devices/-/blob/master/README.md This repository contains all the pre-compiled kernels, kernel modules, and installation scripts necessary for building an installer tailored for a supported device.
- So we will need to clone kali-nethunter-project repository and execute
./bootstrap.shthat will clone kali-nethunter-devices repository todevicesdirectory.git clone https://gitlab.com/kalilinux/nethunter/build-scripts/kali-nethunter-project.git cd kali-nethunter-project/nethunter-installer ./bootstrap.sh # Press enter 3 times to skip and wait until cloning is finished - You can add your unsupported device by following the instructions here: https://gitlab.com/kalilinux/nethunter/build-scripts/kali-nethunter-devices/-/blob/master/README.md
- Now execute the following commands
mkdir kali-nethunter-project/nethunter-installer/devices/thirteen/surya-los cp kali-nethunter-kernel/out/arch/arm64/boot/Image.gz-dtb /kali-nethunter-project/nethunter-installer/devices/thirteen/surya-los cp -r kali-nethunter-kernel/modules_out/lib/modules/ /kali-nethunter-project/nethunter-installer/devices/thirteen/surya-los - Now start build Kali Nethunter for our phone codename with Android 13 and full kali fs.
./build.py -d surya-los -T -fs full - After finishing the build, You will have the kali rootfs archive in file like
nethunter-20230808_034812-surya-los-thirteen-kalifs-full.zipinkali-nethunter-project/nethunter-installerso we can flash it but this time from Magisk Manager.adb push nethunter-20230808_034812-surya-los-thirteen-kalifs-full.zip /storage/emulated/0 - Then open Magisk Manager -> Modules -> Install from storage and select our kali nethunter zip file.

And HERE WE GO, The Custom build of Kali Nethunter is here.

Add RTL8188EU Drivers for TP-Link TL-W722N v2,v3 and ALFA-AWUS036NHA to the Kernel
In the Kali Nethunter documentation they mentioned the following: TP-Link TL-WN722N v1 (Please note that v2 & v3 have unsupported chipsets) but v2 and v3 may be supported using RTL8812AU drivers.) So after doing some researching we need to do the following steps to add support to TP-LINK TL-WN722N v2 which I already have and maybe v3, I didn’t tested yet and ALFA-AWUS036NHA which will supported too.
- Go to the kernel source code “In my case lineageOS kernel” and remove the following directory.
cd android_kernel_xiaomi_surya/drivers/staging rm -rf rtl8188eu vim Makefile # Remove line: obj-$(CONFIG_R8188EU) += rtl8188eu/ vim Kconfig # Remove line: source "drivers/staging/rtl8188eu/Kconfig" - Then in the drivers directory, clone rtl8812au driver source which is RTL8812AU/21AU and RTL8814AU driver with monitor mode and frame injection from aircrack-ng repository.
cd .. git clone https://github.com/aircrack-ng/rtl8812au.git vim Makefile # Add line: obj-y += rtl8812au/ vim Kconfig # Add line: source "drivers/rtl8812au/Kconfig" - After that go up one directory and run and open
kali-nethunter-kernelthen runbuild.shagain and select 3. Configure & recompile kernel from previous run.cd ../kali-nethunter-kernel ./build.sh - Now hit Enter to edit the kernel config
- In section Device Drivers
- Check <M>Realtek 88XXau USB WiFi
- Save and Exit to proceed the kernel recompiling
- After it finishes, Select 6. Create Anykernel zip and it will be available at
kali-nethunter-kernel/output/anykernel-NetHunter.zip - Now flash the custom kernel
adb reboot-bootloader fastboot boot twrp-3.5.2_10-10-surya.img adb push anykernel-NetHunter.zip /bluetooth #Go to install -> Up A Level -> bluetooth -> anykernel-NetHunter.zip and swipe to flash
Now after rebooting, Connect the TP-Link TL-W722N to the phone and open NetHunter application then go to Custom Commands and Launch Wifite.
Select the interface the have Qualcomm Atheros Communications AP9271 802.11n and hit Enter.
-
Testing TP-Link TL-W722N v2

-
Testing ALFA-AWUS036NHA

So finally we are done 💀
Important Links
- LineageOS 20.0 moded and patched kernel source: https://github.com/r0ttenbeef/android_kernel_xiaomi_surya
- Xiaomi Poco X3 NFC Lineage20 support Merge Request to kali nethunter devices: https://gitlab.com/kalilinux/nethunter/build-scripts/kali-nethunter-devices/-/merge_requests/352
- The custom kernel and kali nethunter custom build to download and flash https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/163Jsb31qC9hcbjeCuKz-eyVT6ggeKVyq?usp=drive_link